EE
420L Engineering Electronics II Lab - Lab 6
Single-stage
transistor amplifiers
Pre-lab work
- This lab will utilize the ZVN3306A and ZVP3306A MOSFETs.
- Review these datasheets and become familiar with these transistors.
- Verify that the simulations seen in lab6_sims.zip reasonably model the behavior of the transistors' ID v. VGS, ID v. VDS, and gm v. VGS curves.
- Finally,
watch the video single_stage_amps and review single_stage_amps.pdf
This is a two week lab.
- Below are schematics for NMOS and PMOS source followers amplifiers (also known as common-drain amplifiers).
- In
your lab report discuss the operation of these circuits.
- Simulate the operation
of these
amplifiers.
- Hand calculate, and then verify your hand calculations with experimentation and simulations, the gains and the input and output resistances ensuring that your test signals are at a high enough frequency that the caps have negligible impedance but not so high that the gain is dropping off.
- If
you build this circuit using electrolitic capacitors, assuming
the
input AC signal swings around ground, put the "+" terminal of the cap
on the gate of the MOSFET. Please indicate, in your lab report, that
you understand why the capacitor is connected this way.
- In
your lab report discuss, in your own words, how to measure the
input resistance.
- For
measuring the input resistance add
a resistor equal to the value you calculated
between the input voltage source and the amplifier.
- Measure
the peak AC current through
this added resistor by taking the difference in the peak AC voltages
across the
resistor (on one side is the input voltage signal and the other side is
the
connection to the amplifier's input capacitor) and then dividing by the
resistor's value.
- Measure
the peak AC voltage on the
input of the amplifier (the left side of the capacitor).
- Dividing
this peak AC voltage by the
peak AC current through the added resistor is the amplifier's input
resistance.
- Again,
in your lab report discuss how to measure the
output resistance.
- For
measuring the output resistance,
add a resistor equal to the value you calculated in series with a big
capacitor
(to avoid messing up the biasing) from the amplifiers output to
ground.
- Measure
the peak AC current through
this added resistor.
- Measure
the peak AC voltage (remove
the DC component) on the gate of MOSFET and the peak AC voltage on the
source
of the MOSFET. The difference in these two AC voltages is the peak AC
gate-source voltage of the MOSFET.
- Dividing this peak AC gate-source voltage by the peak AC current through the added resistor is the amplifier's output resistance.
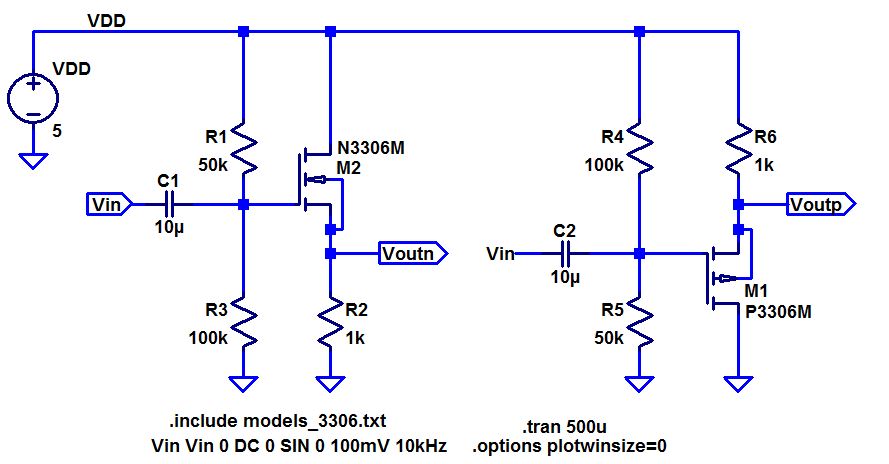
- Below are two common-source amplifiers.
- Discuss the operation of these amplifiers in your lab report including both DC and AC operation.
- Hand calculate the gains and the input/output resistances.
- How
does the source resistance, Rsn or Rsp, influence the gain.
- Again compare your hand calculations to simulation and experimental results.
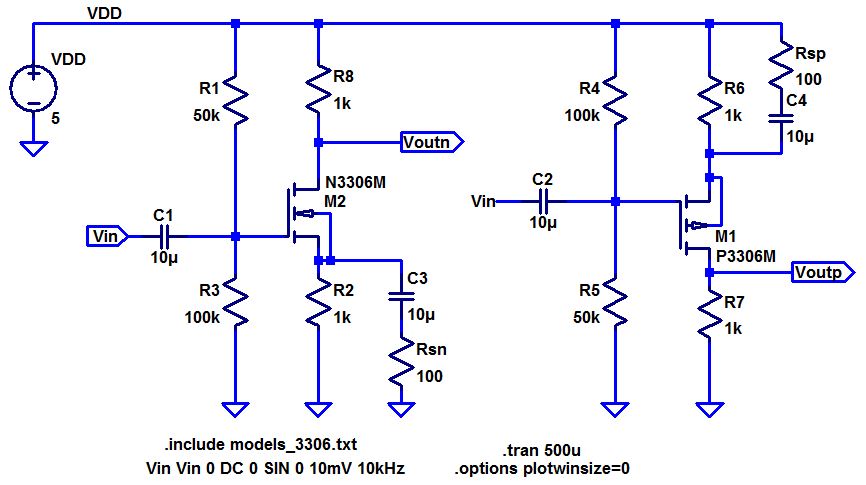
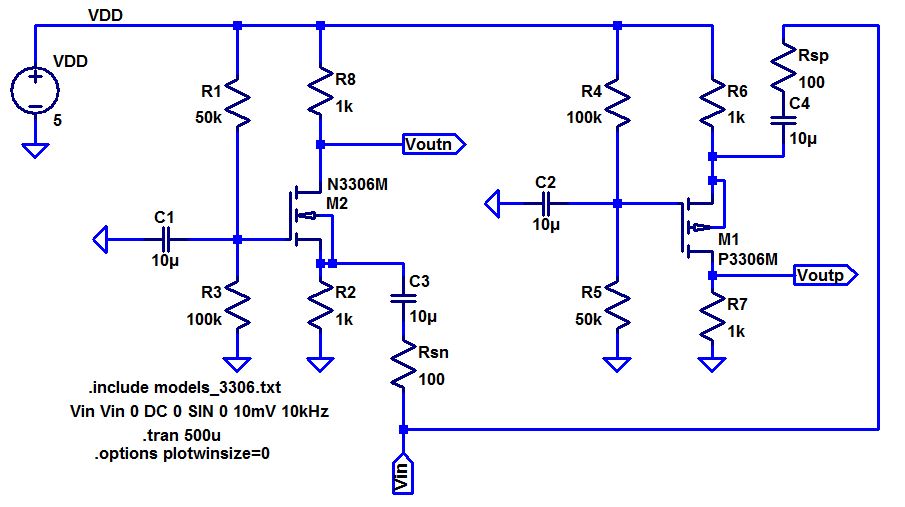
- Below are two common-gate amplifiers.
- Discuss the operation of these amplifiers in your lab report including both DC and AC operation.
- Hand calculate the gains and the input/output resistances.
- How
does the source resistance, Rsn or Rsp, influence the gain.
- Again compare your hand calculations to simulation and experimental results.
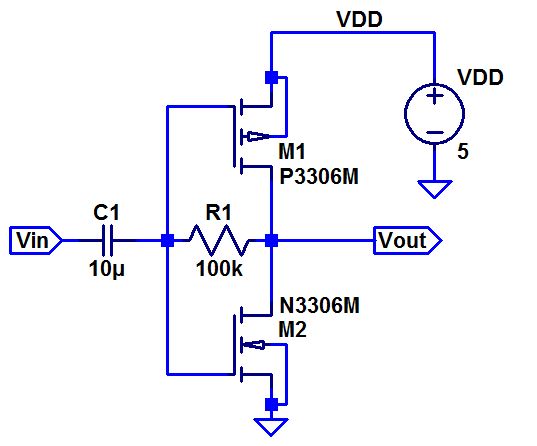
- Below is a push-pull amplifier.
- Discuss the operation of this amplifier in your lab report including both DC and AC operation.
- Hand calculate the gain of this amplifier.
- Do you expect this amplifier to be good at sourcing/sinking current? Why or why not?
- What
happens to the gain if the 100k resistor is replaced with a 510k
resistor? Why?
- Again compare your hand calculations to simulation and experimental results.
- Note
that the gain of this amplifier is large so the output may saturate at
VDD and Ground. To avoid this saturation you can reduce the AC input
voltage using a voltage divider.
Ensure
that your html lab report includes your name, the date, and your email
address at the beginning of the report (the top of the
webpage).
When
finished backup your work.